Biometrics, in its standard version (so-called physical), is a technology based on characteristic static data that is attributed to a single person only. It takes into account such elements as, for example, facial appearance, fingerprints or hand shape, and even the iris of the eye.
So what is behavioral biometrics responsible for? And why could it become the next element in the fight against fraud in e-commerce, finance and digital services?
Check out this article to learn about its definition, types, and application.
What is behavioral biometrics and how does it work?
Behavioral biometrics involves analyzing and measuring human behavior to detect unique patterns that can be attributed to a specific user.
To further illustrate to you the principle of its operation – let us use a practical example. Well, behavioral biometrics can be compared to human fingerprints. Despite the fact that every person has them – finding two people in the world who have exactly the same ones is extremely unlikely.
The same is true for activities that relate to behavioral biometrics. Despite the fact that most of us use our phones or laptops in very similar ways, our behaviors differ in small details that allow us to identify patterns that are unique to a particular person.
In practice, this type of biometrics introduces a new level of user authentication that increases the level of user security, while not requiring users to perform additional actions (such as at least entering a PIN number, password, etc.).
What are the types of behavioral biometrics?
Individual users are distinguished both by how they use a particular device and by their behavior on a particular website or app. Behavioral biometrics considers the following factors:
The way you hold and use your devices (phone or computer)
The use of the following devices is verified:
- Phone – including what position and angle it is in, the intensity and speed with which you tap its screen, and even how and in which direction you move it (e.g., when viewing content or typing in data).
- Mice – including how you move the cursor, the intensity with which you use the buttons, and even how you use the scroll function.
- Keyboards – among other things, how quickly you enter strings of characters, or how you use special characters. Here it is also worth noting that „real” users use keyboards completely differently than bots. While in the case of the latter – the time between clicking the letter „A” and „O”, for example, is basically identical to that between „D” and „C”, in a „live” human it will take a little longer to type the former string of characters. This is all due to the distance between the two keys.
- Login to the account by unauthorized persons (known as account takeover) – for example, to e-banking or to the mobile app of your favorite e-commerce store.
- Entering into a contract for a debt financial instrument (such as a loan) on the data of another person – in order to quickly use the funds thus obtained without the intention of settling the debt.
- Making an order on the data of another person (either on their own or with the help of bots) – choosing a deferred or installment payment, which will then be charged to the data owner. This applies to typical e-commerce purchases as well as, for example, commitments made to telecommunications companies.
- Bot activity – making bulk purchases of discounted products, repeated use of promotions, discount codes or free trial periods, „bulk” applications for loans or other products.
- Non-compliant account sharing – use of paid digital services or products by additional unauthorized persons.
Bottom line: behavioral biometrics works well in all areas vulnerable to fraud. Those in which criminals seek to bring about financial extortion through the use of foreign personal data.
How do we know that a particular behavior risks fraud?
It’s all thanks to artificial intelligence algorithms that analyze a range of behaviors of a given user in real time and identify suspicious activity. Excellent examples of „threatening” behavior include copying a user’s PESEL number or credit card number from the clipboard instead of manually typing it in. This may indicate that the user does not „own” the data (and therefore does not remember it or does not have current access to it), but has merely come into potentially unauthorized possession of it.
However, there are more behavioral characteristics that may indicate a potential risk of fraud. For example, the algorithm may detect that the user is always using the app while holding the phone in his hand. As a result, the device is constantly shifting slightly in space. In comparison, a bot’s use of the app is unlikely to involve any movement in space. Moreover, a normal user rarely holds the phone upside down, while the bot can maintain a constant emulated position (including upside down).
This information, combined with other factors, can be considered anomalous by the algorithm, which gives a clear signal that the particular user may not have entirely pure intentions (or be a bot). Based on this, the system may block the ability of such a user to place orders, or force additional authentication through another method, such as remote verification, sending a verification code to an email address or phone number.
What should you pay attention to?
Of course, it is important to keep in mind that like any technology – this one also has some limitations that need to be identified and then optimized. One of them is the reduced effectiveness of the algorithms when more than one person uses the same account. This makes it difficult to clearly identify the typical behavior of a given user, and thus to identify deviations from the norm resulting from the use of an account by an unauthorized person.
Another of such bottlenecks faced by many companies responsible for behavioral biometrics is so-called „averaging.” Namely, collecting data on tens or perhaps hundreds of thousands of users can lead to a certain „blurring” of information, and thus the attribution of specific behaviors not to one, but to several or a dozen individuals. This, in turn, raises serious concerns about identifying specific users and, by extension, ensuring an adequate degree of security for them.
At Algolytics, we completely eliminate the problem of averaging, because we do not focus only on elements that are similar, but also on those that unambiguously distinguish between users. Such an action can be compared, for example, to character analysis, which carefully examines the handwriting and then picks up the nuances that make it possible to unambiguously determine who is behind a given handwriting (or in the case of behavioral biometrics, simply behavior).
Behavioral biometrics and its impact on security – summary
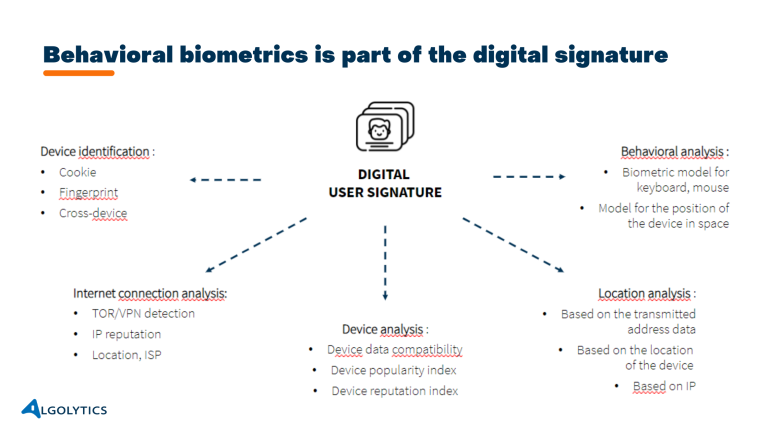
Biometrics, which we have discussed, in this text is part of what is known as a user’s digital signature, which in addition to analyzing the user’s behavior, also takes into account factors such as the user’s location, the device used and even the Internet connection. All of this information combined makes it possible to create even more precise fraud or default prediction models for a given transaction.
If you’re looking to improve security while providing an even better user experience for your systems and applications – feel free to contact us. Our experts will be happy to provide you with ready-made solutions that will also work for your organization.

















