Sometimes it is necessary to ask the user for additional information when a script is executed. This can be chieved using the InputDialog Java class. Input dialogs are especially useful in context scripts.
To use the InputDialog class, include the InputDialog Java library from biz.sc.gornik.script.
An InputDialog object is constructed in the usual way. The parameter for the constructor is a string which will appear as the caption in the dialog box titlebar.
The following methods can be used with an InputDialog object:
-
add(text, default, type, required) Adds an input element to the dialog. Input elements are indexed from 0. Only the first argument is mandatory.
text - a string which will be displayed to the left of the input element.
default - the default value displayed in the text element. It can be a number, string or list. In the last case, the user will be able to select from among the elements of the list as well as enter a different value.
type - determines the type of variable that will be returned. The possible choices are:
InputDialog.STRING - returns a string (default).
InputDialog.INT - returns an integer number.
InputDialog.FLOAT - returns a floating-point number,
InputDialog.BOOL - displays a check box and returns an integer equal to either 0 (box not checked) or 1 (box chcecked),
InputDialog.PATH - lets the user enter or select a path to a file or directory and returns a string containing this path.
Note
To set the current user's home directory as the default for this type of input element usejava.lang.System.getProperty('user.home')as the second argument of the add method.
required - if 1, user input in this field is necessary. Default: 0 (the field may remain empty).
-
get(index)orget(text) Returns the value entered by the user in the input element identified by index or text.
-
setDescription(description) Causes the text in description to be displayed in the input dialog.
-
showDialog() Causes the dialog box to be displayed on the screen, so the user can input the requested information.
-
wasCanceled() Return 1 if the user pressed the Cancel button on the dialog box or closed the window and 0 if the user pressed the Run button.
Example 14.33. Creating a basic input dialog
from biz.sc.gornik.script import InputDialog
i = InputDialog('Example input dialog', 0)
i.setDescription('This is a simple input dialog')
i.add('Text input:', 'Default text', 1) #input in this field is mandatory
i.add('Combo box:', [1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6], InputDialog.FLOAT)
i.showDialog()
if not i.wasCanceled():
print i.get(0), i.get('Combo box:')
else:
print 'Script aborted'
Sample output:
Default text 1.4
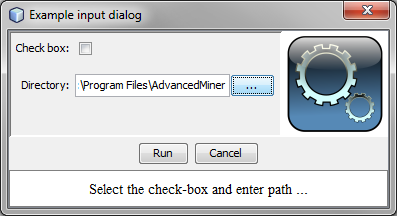
Example 14.34. Creating an input dialog with a check-box and file path field
from biz.sc.gornik.script import InputDialog
i = InputDialog('Example input dialog', 0)
i.setDescription('Select the check-box and enter path ...')
i.add('Check box:', 0, InputDialog.BOOL)
i.add('Directory:', java.lang.System.getProperty('user.home'), InputDialog.PATH)
i.showDialog()
if not i.wasCanceled():
print i.get(0)
print i.get(1)
else:
print 'Script aborted'
Sample output:
1
C:\Program Files\AdvancedMiner