To estimate a vector
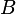 a likelihood function has been introduced
that depends only on the parameters to be estimated. The actual form of
the likelihood function depends on the variant of the model. For the
full observability (non-censored) bivariate probit model it is:
a likelihood function has been introduced
that depends only on the parameters to be estimated. The actual form of
the likelihood function depends on the variant of the model. For the
full observability (non-censored) bivariate probit model it is:
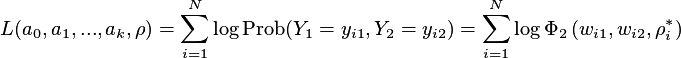
where
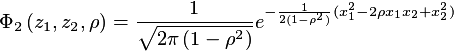
is the bivariate normal distribution:
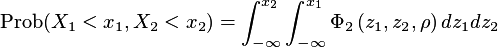
and
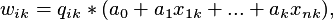
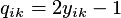
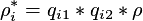
For the partial observability (censored) bivariate probit model the likelihood function has the following form:
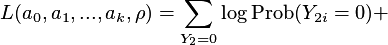

In order to find the solution of the maximization problem for the partial likelihood the module applies the widely used Newton-Raphson algorithm, which tries to zero the first order partial derivatives of the log-likelihood.
The Berndt, Hall, Hall, and Hausman estimator (the so-called BHHH estimator: for details see Berndt et al. 1974) is used to estimate the parameters of the model. The information matrix is approximated by the outer product of the gradient calculated as:
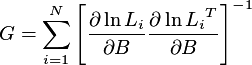
where
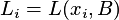 and the BHHH estimators uses the inverse matrix of
and the BHHH estimators uses the inverse matrix of
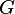 .
.
For testing the global significance of the estimated parameters
(null hypothesis that
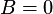 ) three statistics are calculated:
) three statistics are calculated:
All three statistics have an asymptotic chi-squared distribution
with the number of degrees of freedom equal to the dimension of the
vector
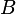 .
.
For testing a linear hypothesis about the estimated parameters (null
hypothesis that
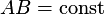 , where
, where
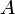 is a matrix of linear coefficients for the
null hypothesis), the
Wald statistic for parameter estimator is calculated.
Under the null hypothesis the Wald statistic has an asymptotic chi-square distribution
with the number of degrees of freedom equal to the rank of the matrix
is a matrix of linear coefficients for the
null hypothesis), the
Wald statistic for parameter estimator is calculated.
Under the null hypothesis the Wald statistic has an asymptotic chi-square distribution
with the number of degrees of freedom equal to the rank of the matrix
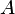 .
.
Under the null hypothesis that
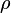 equals zero, the model consists of two
independent logistic probit equations, which can be estimated
separately. Thus, for testing for the absence of the correlation the
following form of Langrange multipliers is introduced:
equals zero, the model consists of two
independent logistic probit equations, which can be estimated
separately. Thus, for testing for the absence of the correlation the
following form of Langrange multipliers is introduced:
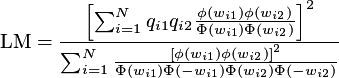
Under the null hypothesis, this test has approximately the chi-square distribution with one degree of freedom.
The confidence interval for the parameters estimates is calculated
for
Confidence Level=
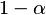 specified in the current algorithm
settings. The upper and lower bounds are calculated as:
specified in the current algorithm
settings. The upper and lower bounds are calculated as:
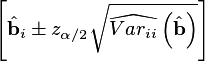
where
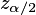 is
is
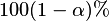 percentile of the standard
normal distribution, and
percentile of the standard
normal distribution, and
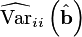 are the i-th diagonal elements of the estimators covariance
matrix.
are the i-th diagonal elements of the estimators covariance
matrix.